⚙️ User-Friendly Automation in IoT
Once IoT devices are connected to a platform, they need to deliver tangible benefits to their users. These benefits can be informational—such as monitoring the temperature inside a home or a greenhouse—or actionable, like opening or closing a valve, controlling a garage door, or turning on an appliance.
While such actions can enhance the quality of life, the true potential lies in automation. Automating processes removes the need for users to perform repetitive or time-sensitive tasks manually, letting programs or pre-configured interactions take care of them instead.
Automation can be implemented in several ways. One common method involves writing code—an approach that's often inaccessible to the average user. To bridge this gap, platforms like IFTTT or Google Home offer simplified automation options. These typically work by linking one device’s state to another’s—for example, turning on a light when another one is activated, or when a specific button is pressed.
However, these basic systems may not be adequate for more complex smart environments. For instance, a smart greenhouse might need to manage internal temperature, regulate sunlight exposure, and monitor fertilizer levels in both water and soil. Such scenarios call for more advanced solutions.
One promising approach is visual programming. Visual programming allows users to create logic flows through intuitive interfaces—such as connecting blocks with lines or nesting them to define behavior—without writing traditional code.
On this page, we'll explore various visual programming tools and platforms you can use to bring powerful automation to your smart home!
Blockly
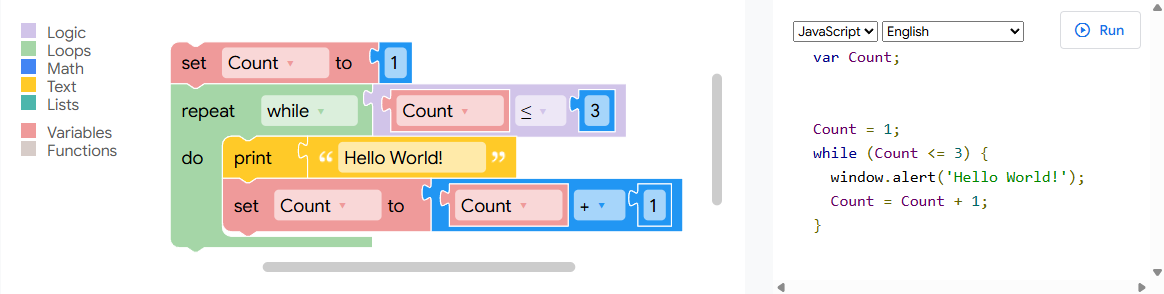
Blockly is a visual programming tool originally developed by Google for use on the web. It allows users to create code by arranging blocks in a simple drag-and-drop interface. Each block represents a logical element—such as loops, conditionals, variables, or actions—which fit together like puzzle pieces. This visual approach makes programming more accessible, especially for beginners or non-technical users.
One of Blockly’s biggest advantages is that it abstracts away the complexity of traditional coding syntax. Instead of worrying about typos or formatting errors, users can focus purely on the logic and structure of their program. This is particularly valuable in educational environments, where students can quickly grasp programming concepts without needing to learn a full programming language first.
Blockly also plays a powerful role in IoT system development. In smart home or smart agriculture applications, for example, users can rapidly prototype device behaviors—like responding to sensor inputs or scheduling device actions—by visually linking logical steps. Some IoT platforms even integrate Blockly as a core part of their automation systems, empowering users to create routines without writing any code.
Moreover, Blockly is highly customizable and language-agnostic. Developers can extend it with their own blocks, and the underlying code can be exported to multiple languages such as JavaScript, Python, PHP, Lua, or Dart. This makes it not only a great learning tool but also a flexible option for rapid development and real-world deployment.
In summary, Blockly is a versatile and beginner-friendly visual programming tool that lowers the barrier to entry for both education and IoT development, helping users focus on what really matters: building functional, intelligent systems.
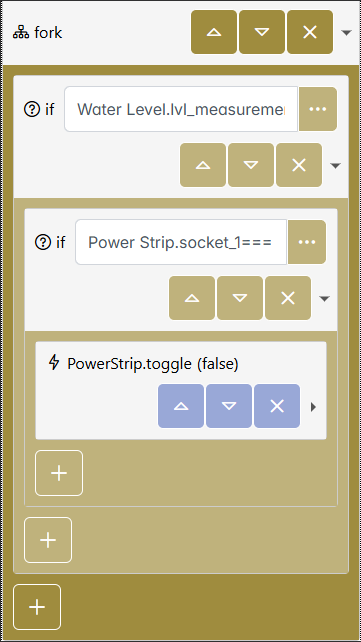
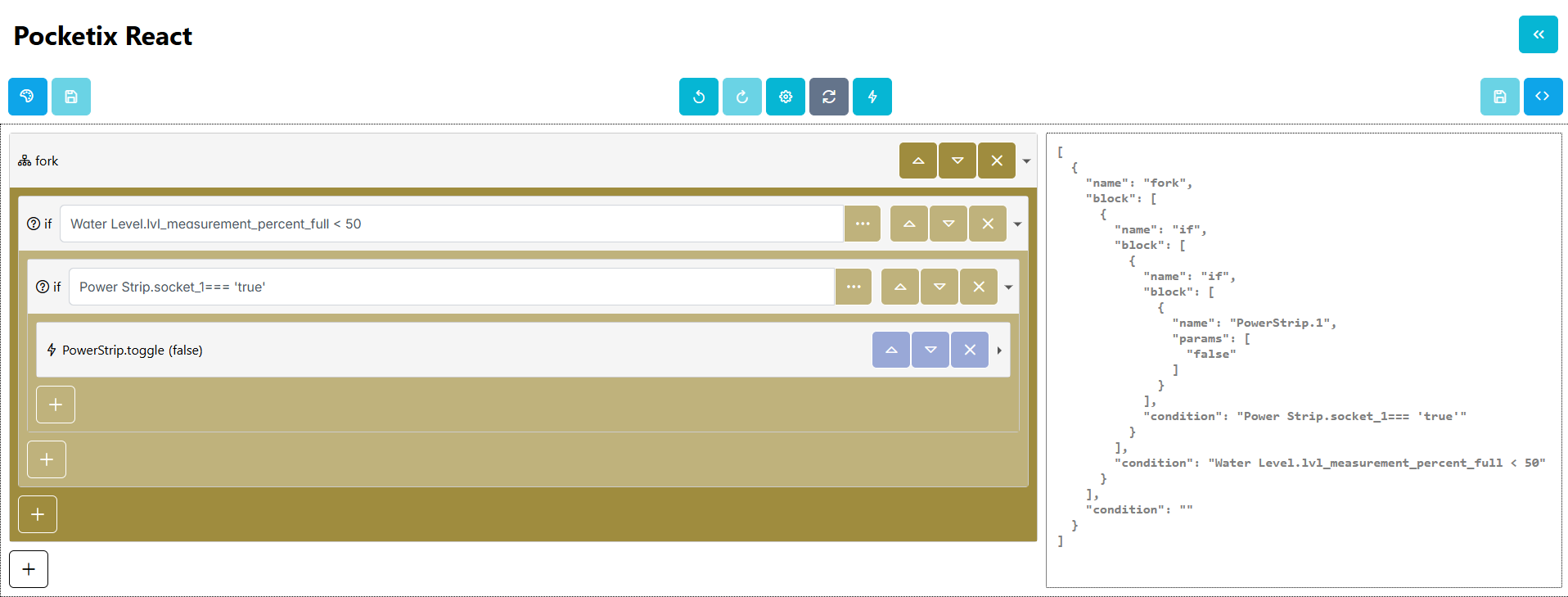
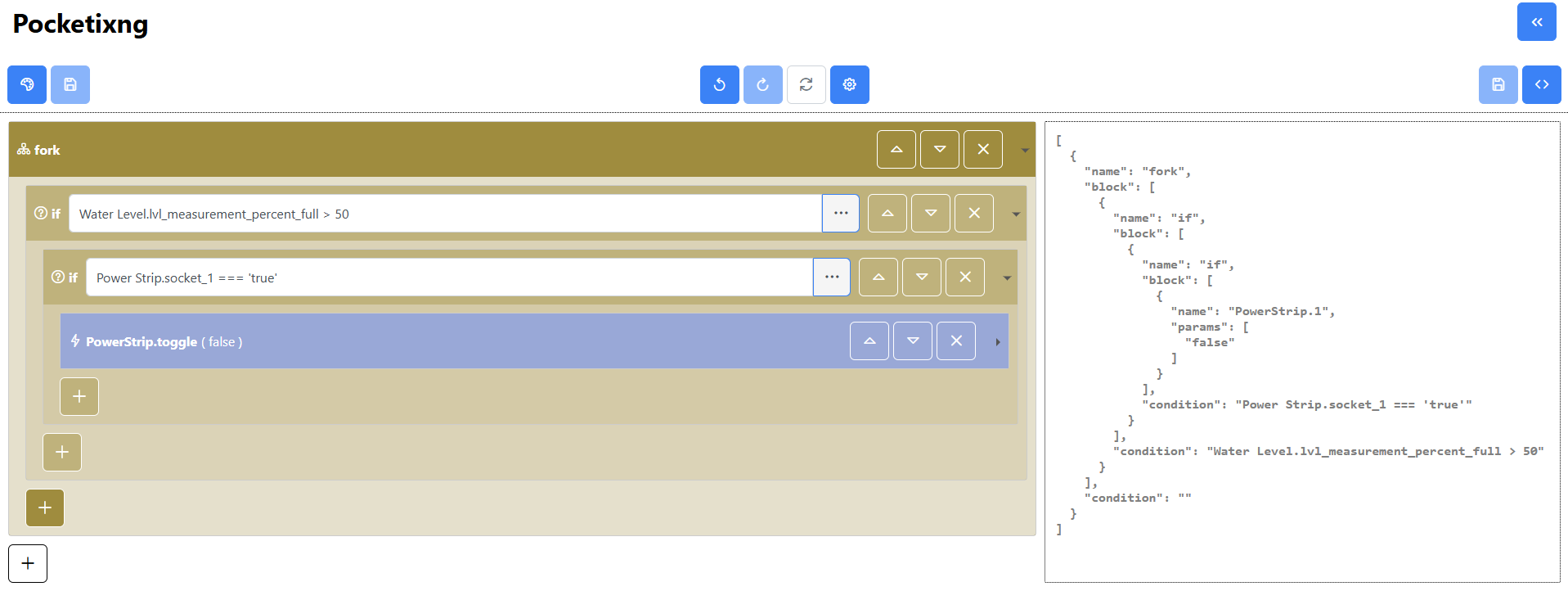
Pocketix
Pocketix is an emerging visual programming editor designed specifically for mobile devices and users who are not
familiar with traditional programming. The platform simplifies the programming experience by allowing users to construct
valid programs using a curated set of blocks. Each block represents a fundamental programming construct, such as
conditionals (if, else), variables, and other control structures, enabling users to build more complex
procedures through nested block configurations—all without the risk of creating invalid code.
Recognizing that complex interactions (like drag and drop) can present challenges for older adults or those new to programming, Pocketix replaces these gestures with straightforward button-based interactions, thereby streamlining the user experience. For advanced users who desire more flexibility, the platform also offers an option to directly edit the code in a JSON-serialized format, bridging the gap between visual programming and traditional code editing.
Although Pocketix is still in its early stages, the development roadmap is rapidly expanding. A completely new editor is currently in the works, featuring a more mobile-friendly design and a range of powerful new capabilities. This includes the development of a visual debugger—a critical tool for helping users better understand and troubleshoot their programs. The debugger is being built alongside a new language, whose interpreter is being written in Go, chosen for its efficiency and scalability.
In addition to debugging, the upcoming editor will introduce:
- Rule recommendations to help users write better logic
- A simple IFTTT-style mode for easy automation
- Usage tracking features to help the development team identify pain points and improve the experience over time
These enhancements aim to make Pocketix not only a learning tool, but a practical and intelligent automation environment for users of all ages and skill levels.
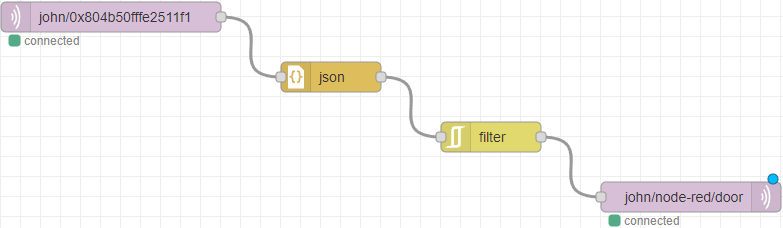
Node-RED
Node-RED is a powerful open-source platform designed for wiring together IoT devices, APIs, and online services in a visual and intuitive way. Built on Node.js, it provides a flow-based, low-code development environment that enables users to build automations and data-driven applications by simply dragging and dropping components on a canvas and connecting them with virtual "wires."
At the heart of Node-RED’s interface are nodes and wires. Each node represents a discrete function or capability—this could be anything from reading a sensor, making an HTTP request, or transforming data. Nodes are categorized by their function, such as input, output, processing, or integration with external services.
Wires are the connectors between these nodes and play a critical role in defining the flow of data. When a node
completes its task (e.g., reading a value or performing a calculation), it sends a message object (msg) along the
connected wire to the next node. This message is typically a JSON object and may contain payloads, headers, or metadata.
The path that wires define effectively models the logic of your application, making it clear how data moves and is
transformed from start to finish.
For example, a simple flow might involve:
- An inject node to trigger an action at regular intervals
- A function node that processes or modifies the data
- A debug node to display the result
By connecting these with wires, Node-RED users can create powerful logic chains that respond to real-time inputs, such as sensor readings, user actions, or network events.
This wire-based programming model enables rapid prototyping and deployment of event-driven systems without requiring traditional code-heavy development. While it’s highly accessible to beginners, Node-RED also supports advanced features like custom function nodes (written in JavaScript), persistent data, user-defined subflows, and secure communication—making it a valuable tool for both hobbyists and professional developers alike.
Node-RED is particularly well-suited for scenarios such as:
- Home automation
- Industrial IoT monitoring
- API orchestration
- Real-time dashboards
- Cloud service integration
Its visual approach, extensibility, and active community make it a leading choice for building smart, connected applications with minimal effort.
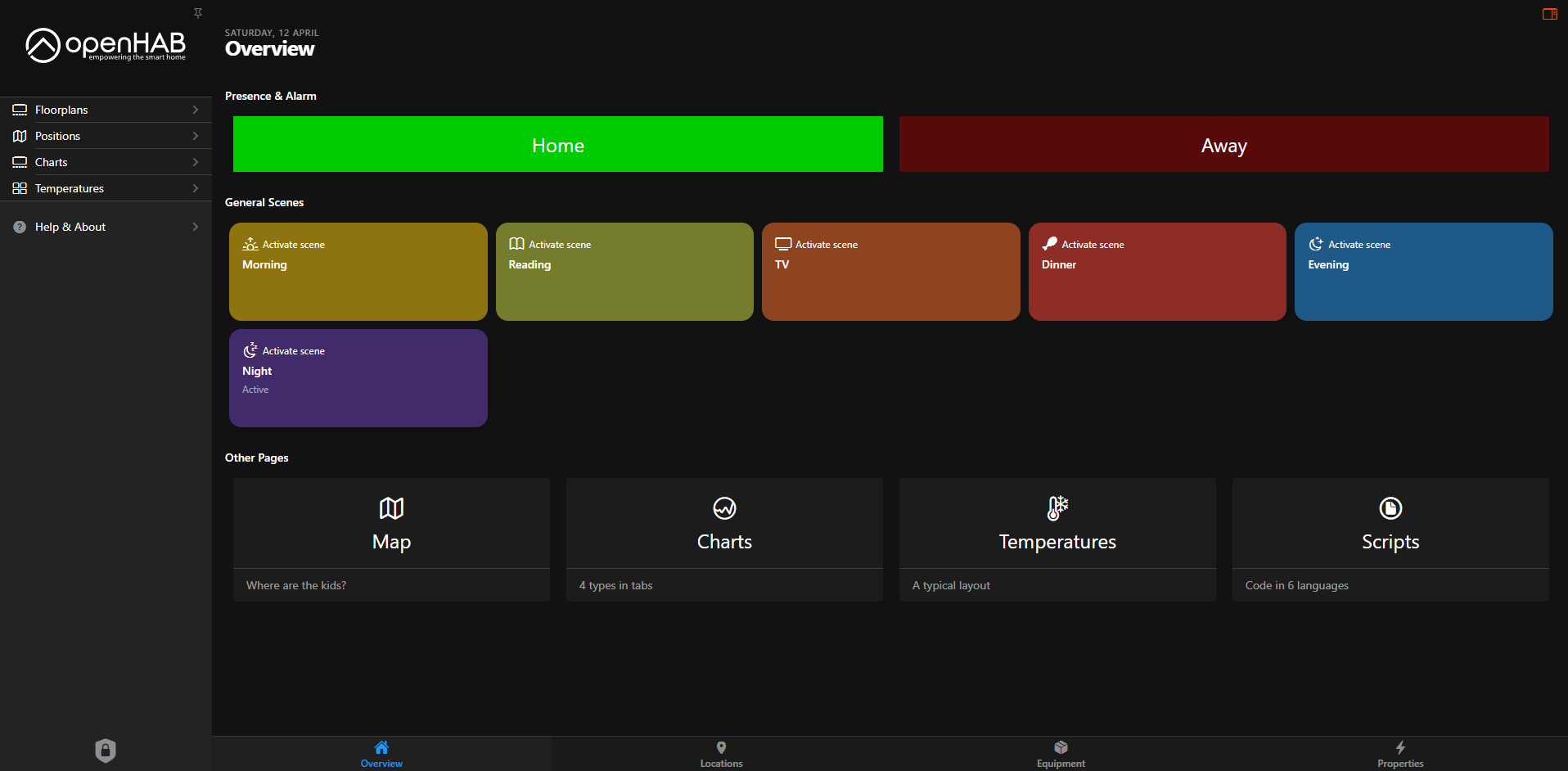
OpenHAB
OpenHAB (Open Home Automation Bus) is a highly versatile, open-source platform designed for integrating, controlling, and automating a wide range of smart home devices and technologies. Built with modularity and interoperability in mind, OpenHAB acts as a central hub for smart home ecosystems, enabling seamless communication between devices from different manufacturers, all within a unified interface.
What sets OpenHAB apart is its support for numerous communication protocols and standards, including Z-Wave, Zigbee, MQTT, KNX, Modbus, and many more. This broad compatibility allows users to bring together a wide variety of IoT devices—lighting, sensors, thermostats, alarms, cameras, appliances—regardless of brand or underlying protocol.
A core feature of OpenHAB is its powerful rule engine, which lets users define sophisticated automation logic using either a graphical interface, domain-specific rule language, or scripting languages like JavaScript and Blockly. These rules can react to triggers such as time events, sensor input, device status changes, or even user presence to perform actions across the home. For example, OpenHAB can automatically:
- Turn off all lights when no one is home
- Send an alert when a door is opened during nighttime
- Adjust the thermostat based on current weather and time of day
The platform is designed with both beginners and advanced users in mind. Casual users can take advantage of the intuitive UI and predefined automation templates, while power users can dive into custom scripting and fine-tuned configurations to suit complex needs.
In addition to automation, OpenHAB offers:
- Dashboards and UI customization for creating personalized control panels
- Voice assistant integration (Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, Apple Siri)
- Remote access via mobile apps and cloud connectors
- A rich add-on ecosystem with bindings for thousands of devices and services
Thanks to its vendor-neutral approach and a strong, global open-source community, OpenHAB continues to evolve rapidly. It's particularly favored by smart home enthusiasts, tinkerers, and professionals who require a robust, privacy-conscious solution that puts users fully in control of their environments—free from proprietary lock-in.
Whether you're looking to automate a single room or orchestrate an entire smart building, OpenHAB provides the flexibility, scalability, and transparency to make it possible.


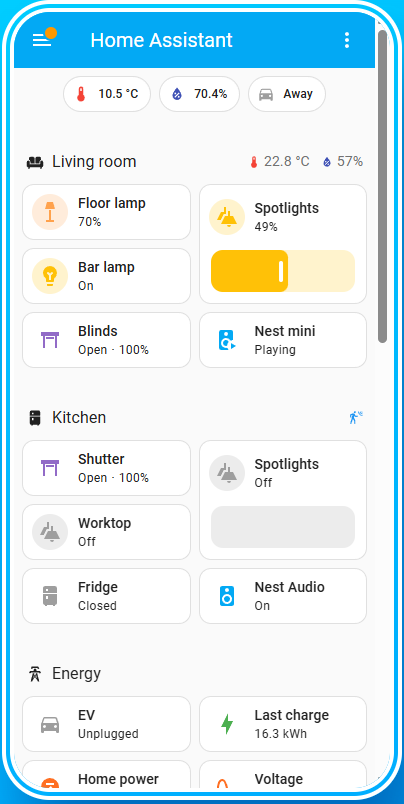
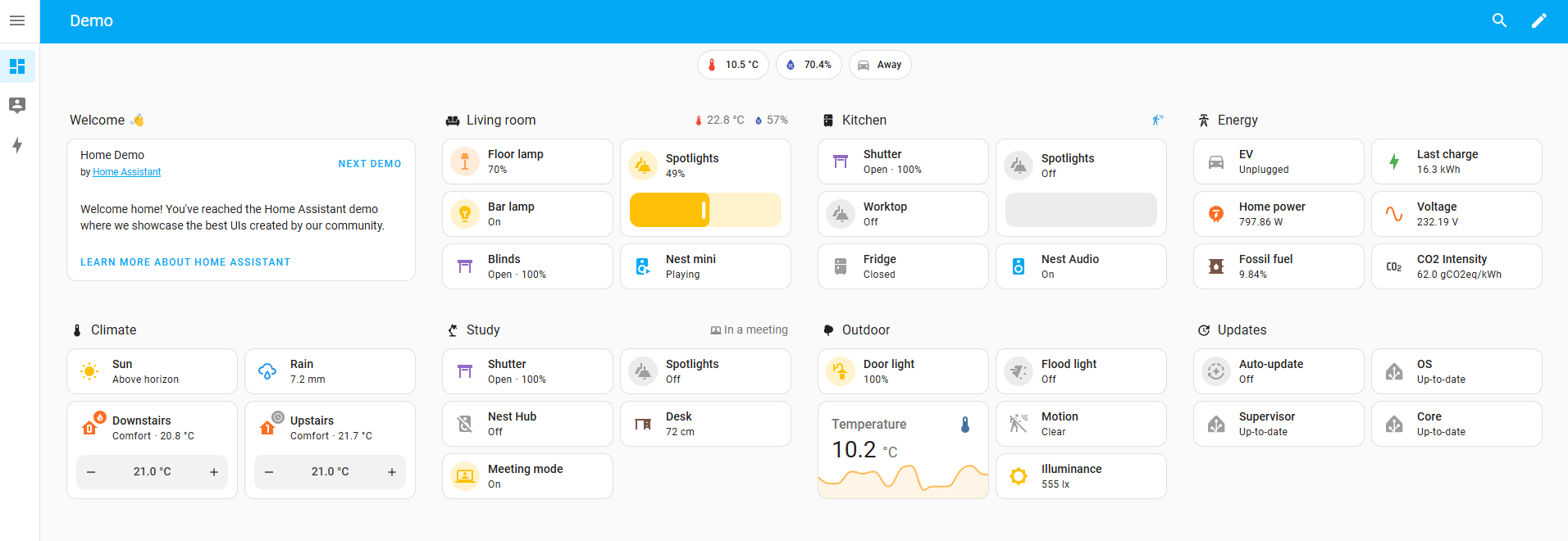
Home Assistant
Home Assistant is a powerful and increasingly popular open-source platform for building and managing smart home systems. Designed with a focus on privacy, local control, and flexibility, Home Assistant gives users full ownership over their data and automations, while still offering the convenience of optional cloud integrations. Whether you're just starting with smart devices or orchestrating a complex, multi-room automation setup, Home Assistant offers a scalable solution tailored to your needs.
Like OpenHAB, Home Assistant supports a vast array of IoT devices, protocols, and services, including Z-Wave, Zigbee, MQTT, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi-based devices, and many cloud services like Google Assistant, Amazon Alexa, and Apple HomeKit. Its rapidly growing ecosystem of integrations—powered by a vibrant and active community—ensures that new devices are added frequently, keeping pace with the fast-moving smart home landscape.
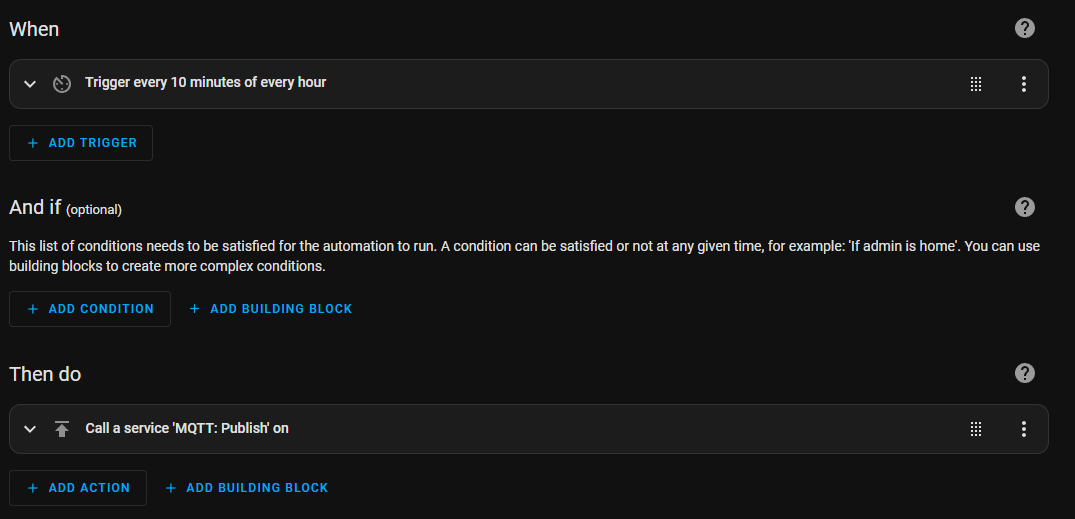
Home Assistant’s automation engine allows users to create event- and condition-based rules that dictate how devices behave. Automations can be built using a simple visual editor or written in YAML for more granular control. For example, users can set up scenarios such as:
- Automatically turning off lights when no motion is detected for a certain period
- Sending a notification if a window is open when it starts raining
- Adjusting climate settings based on time of day or presence detection
Some key features of Home Assistant include:
- Local-first architecture: All data and automation run locally by default, which not only protects user privacy but also ensures faster and more reliable performance—even when the internet goes down.
- User-friendly web interface (Lovelace): Highly customizable dashboards let users design their own control panels for different rooms, devices, or use cases.
- Mobile apps for iOS and Android: Offering full control, presence tracking, and notification support directly from smartphones.
- Extensive automation options: Including triggers based on time, state, geolocation, device events, and more.
- Add-on system: Supports extensions like Node-RED, ESPHome, and custom integrations, further expanding Home Assistant’s capabilities.
Home Assistant also offers Home Assistant Cloud (via Nabu Casa), a privacy-conscious optional subscription service that simplifies remote access, voice assistant integration, and secure external connections—without the need for complex network configuration.
With its strong emphasis on transparency, reliability, and community-driven development, Home Assistant has become a go-to solution for smart home enthusiasts, makers, and professionals. It empowers users to create fully customized, intelligent environments while staying in control of how their data is collected, stored, and used.
Whether you're automating a few lights or building a fully autonomous home, Home Assistant provides a solid, flexible foundation that grows with your smart home ambitions.
The Importance of User-Friendly IoT Automation
As IoT ecosystems become increasingly complex, the need for intuitive, user-friendly automation tools has never been more critical. Platforms like Blockly, Pocketix, Node-RED, OpenHAB, and Home Assistant bridge the gap between technical experts and everyday users, making it possible for anyone to design, configure, and control their smart environments with minimal technical knowledge. By offering visual interfaces and low-code solutions, these tools empower users to create intelligent systems, allowing them to focus on the functionality and usability of their IoT setups rather than the intricacies of traditional programming.
Whether you're a novice looking to get started with IoT or an experienced developer seeking to streamline your automation processes, these platforms provide the tools and flexibility needed to build the next generation of connected systems.